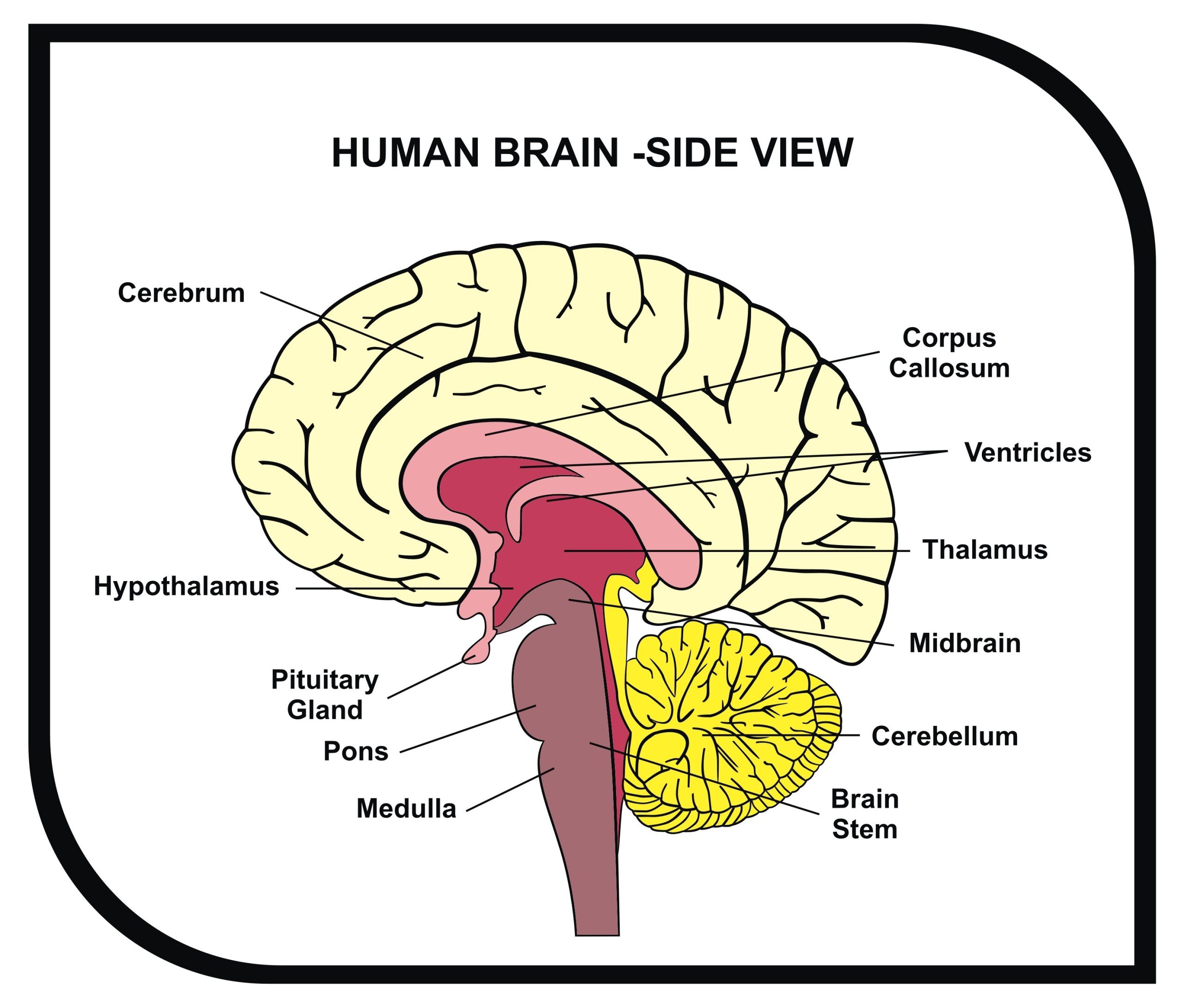
Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor (BDNF) is a protein produced in the brain that plays an essential role in neuronal growth, development, and maintenance. It is essential for the growth and survival of neurons and for the formation of synaptic connections between them. BDNF also has a role in learning and memory formation by influencing neurotransmitter release at synapses. Also, it is involved in regulating mood and mental health.
BDNF is synthesized in various brain regions, including the hippocampus, cortex, striatum, hypothalamus, and olfactory bulb. It is released from nerve cells when they are stimulated, leading to increased activity at nearby synapses which can help strengthen those connections. This process is known as long-term potentiation (LTP).
Also, BDNF binds to two different types of receptors on the surface of neurons: TrkB receptor and p75 receptors. The binding to TrkB activates pathways which lead to enhanced neuronal excitability and plasticity; whereas binding to p75 leads to cellular death or apoptosis when there is excessive stimulation.
Low levels of BDNF linked to increased risk for mental health issues
Research suggests that Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor influences neuronal plasticity throughout life – from early development until late adulthood – though the exact mechanisms remain uncertain. Additionally, some evidence indicates altered levels of BDNF may be associated with psychiatric disorders like depression and schizophrenia. Low levels of BDNF have been linked to increased risk for depression and other mental health issues like Alzheimer’s disease. However, higher levels of BDNF may promote better cognitive function and improved mental well-being.
How does BDNF function within the brain?
Understanding how BDNF functions within the brain could potentially bring about new avenues for developing treatments for these conditions. It is an important protein that plays a vital role in several bodily processes. Knowing your BDNF levels can provide useful information about your brain health and may help you make informed decisions about lifestyle changes to promote better mental wellbeing.
BDNF levels are primarily determined by genetics, but nutrition, physical activity, and lifestyle factors can also influence them. It is released into the bloodstream and can be detected with a lab test. In general, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor levels tend to decrease over time due to age-related changes and the onset of certain health conditions.
The most reliable way to measure BDNF levels is through blood tests at a laboratory. This requires taking a blood sample from the arm or finger which is then analyzed in a lab for BDNF concentrations.
Ways to improve BDNF levels
Increasing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is essential for maintaining healthy brain cells, as it plays a key role in the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons.
There are several ways for people to boost their BDNF levels and support their brain health. For starters, regular physical exercise is a fantastic way to increase BDNF levels. Studies have shown that 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise can significantly boost BDNF concentrations in both young and elderly adults. Other forms of physical activity such as yoga, resistance training, tai chi, and qigong may also provide similar benefits for your brain health.
Some research suggests that nutritional supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids may help increase BDNF production in the brain, although more evidence is needed before it can be recommended as an effective treatment option.
In addition to regular physical activity, other lifestyle choices such as getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins, reducing stress levels, and avoiding drugs or excessive alcohol intake can also help support good mental health by maintaining balanced BDNF levels in the body.
Eating a healthy diet is another crucial factor for increasing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor levels. Eating plenty of antioxidant-rich foods like berries and dark leafy greens has been linked with increased BDNF production in the body. Research also suggests that certain vitamins and minerals may be beneficial for boosting BDNF levels. Examples include omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, zinc, and magnesium.
Finally, getting plenty of quality sleep is another key factor for increasing BDNF levels. Studies show that optimal sleep duration (7-9 hours) can help to increase BDNF concentrations in the body. Additionally, implementing a regular bedtime routine with practices such as winding down before bed and avoiding blue lights and device screens helps to promote healthy sleep habits and boost BDNF production.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily life, you can significantly improve your brain health by increasing BDNF levels. Taking the time to invest in your brain health now will pay dividends later in terms of mental sharpness and overall well-being.